A digital diploma is the electronic version of your academic credential. It contains the same information as a paper diploma, but includes built-in verification technology that proves its authenticity. Major U.S. universities like MIT, UCLA, and Temple University now issue digital diplomas alongside traditional paper versions. If you're applying to graduate school or entering the job market, you need to understand how these credentials work and whether they'll be accepted.
What Makes a Digital Diploma Different
A digital diploma is not a scanned copy of your paper certificate. It's a secure electronic file that contains your degree information, graduation date, and institution details. The file includes cryptographic signatures and unique identifiers that allow anyone to verify its authenticity in seconds.
UCLA, for example, issues what it calls a CeDiploma. Each one contains a unique 12-digit identifier. Employers or graduate schools can enter that code on UCLA's validation page to verify diploma authenticity instantly. The document is digitally signed and encrypted, making it tamper-proof.
This differs from a traditional paper certificate in a fundamental way. Paper documents can be forged, lost, or damaged. Replacement degree or diploma certificates can cost between $25 to $150 each time, with delays in receiving replacements and risk of loss in the mail. Digital diplomas eliminate these problems. Once downloaded, your credential is always accessible and verifiable.
Some institutions use blockchain technology to secure their digital diplomas. MIT became one of the first universities to issue recipient-owned virtual credentials using Bitcoin's blockchain technology. With blockchain, a record of your diploma exists on a distributed ledger that cannot be altered or deleted. This provides an extra layer of security beyond standard encryption.
How Verification Works
Three parties are involved in digital credential verification: the issuing institution, the credential holder (you), and the verifier (an employer or graduate school).
When your university issues a digital diploma, it creates a cryptographic signature tied to your credential. According to Diplomasafe, anyone can access the blockchain and verify the authenticity of a certificate by comparing the digital signature with the one recorded on the blockchain. This transparency allows employers and schools to independently confirm validity without relying on a phone call to the registrar's office.
For credentials not secured by blockchain, verification typically works through the issuing institution's portal. You share a link or unique code with the verifier. They enter it on the university's website and receive instant confirmation of your degree.
The National Student Clearinghouse is the trusted source for education verification, offering a nationwide collection of enrollment and degree data. This organization verifies credentials for most U.S. colleges and universities. Many employers and graduate programs use this service to confirm applicants' degrees.
Traditional verification methods often take days or weeks. According to Certifaction, the average waiting time per verification request for an educational institution is 60 minutes, and the usual waiting time for the employer is 1-2 weeks. Digital verification reduces this to seconds.
Do U.S. Universities Accept Digital Diplomas?
Yes. U.S. universities accept digital diplomas from accredited institutions. The format of your credential does not determine its legitimacy. Accreditation does.
When you apply to graduate school, the admissions office cares about two things: whether your degree came from an accredited institution and whether you completed the requirements. A digital diploma from an accredited university carries the same weight as a paper one.
According to U.S. News, students in online programs usually earn the same degree as on-campus students. The curriculum for an online bachelor's degree typically matches the on-campus curriculum at the same school, and the diploma usually doesn't state whether that specific degree was earned online or in person.
This applies whether you earned your degree online or in person. The delivery method of your education and the format of your diploma are separate issues. An online degree from a regionally accredited university is legitimate. A digital diploma from that same university is equally legitimate.
Regional accreditation is the gold standard. According to OnlineU, the Higher Learning Commission, formed in 1895, is one of the oldest and most respected regional accrediting bodies for postsecondary education. Other regional accreditors include the Middle States Commission on Higher Education and the WASC Senior College and University Commission. If your institution holds accreditation from one of these bodies, your digital diploma will be accepted.
Be cautious of diploma mills. OnlineU warns that a few online schools known as "diploma mills" are not legitimate, and one way these schools try to disguise themselves is by proclaiming accreditation that's actually from a fictitious agency. Always verify your institution's accreditation through the U.S. Department of Education database before enrolling.
How Long Are Digital Diplomas Valid?
Digital diplomas from accredited institutions do not expire. According to UCLA, once downloaded, the digital diploma does not expire; it is valid for life.
This differs from technical security certificates used for websites. According to DigiCert, SSL/TLS certificate validity periods are currently 398 days, or about 13 months. These are scheduled to decrease to 47 days by 2029. But these are not the same as academic credentials. Your digital diploma remains valid indefinitely.
The underlying verification infrastructure may change over time. If your university switches platforms or updates its verification system, your credential should still be verifiable. Blockchain-secured diplomas are particularly resilient because the verification data exists on a distributed network rather than a single server.
Best practice: Download your digital diploma and store it in multiple secure locations. Keep a copy on your computer, in cloud storage, and on an external drive.
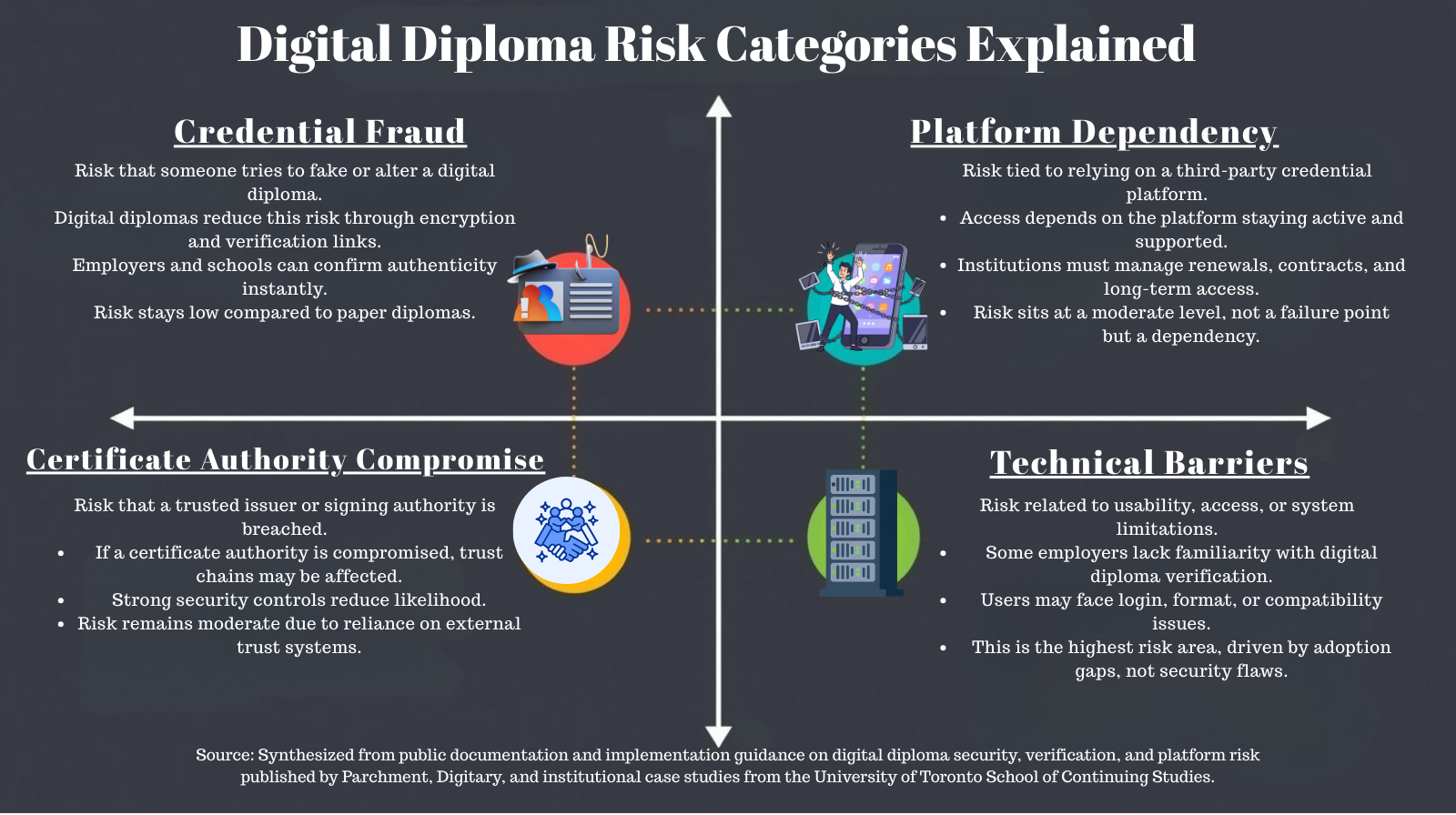
The Risks You Should Know
Digital diplomas are more secure than paper, but they're not without risks.
Credential fraud still exists. According to Certifaction, searching for "fake diplomas" on Google brings up over 24 million search results. Simple PDF diplomas without verification technology can be forged. This is why blockchain-secured credentials and institutional verification portals matter. A legitimate digital diploma includes a way to verify it.
Platform dependency. If the verification platform shuts down or the issuing institution closes, access to verification could be disrupted. According to Campus Technology, institutions like ECPI University use digital credentialing services like Parchment to manage credentials. If such a service experienced problems, verification could be temporarily unavailable.
Certificate authority compromise. According to Portnox, if a trusted CA is compromised, attackers can issue fake certificates for legitimate websites. While this risk applies more to web security certificates than academic credentials, any digital system has potential vulnerabilities.
Technical barriers. Some employers or institutions may be unfamiliar with digital credentials. You might need to explain how to verify your diploma or provide a paper copy alongside the digital version.
To protect yourself:
Use credentials from accredited institutions only
Verify through official channels (institution websites, National Student Clearinghouse)
Keep backup copies of your digital diploma
Be prepared to explain the verification process to unfamiliar recipients
What Digital Diplomas Cost
For students, digital diplomas typically cost nothing extra. Most U.S. universities that offer them include the digital version at no additional charge when you graduate.
According to UCLA, students can obtain a secure digital diploma in addition to the traditional paper diploma at no additional cost. This is the standard approach at most institutions.
The costs fall on the institutions, not the students. Universities pay for digital credentialing platforms based on volume. According to Certifier, issuing 500 certificates costs around $2,500 on some platforms, and plans go up to 10,000 annual badges for $20,000. That works out to roughly $2 per credential.
Some platforms offer more affordable options. Certifier reports that the Starter Plan is free and allows you to issue up to 250 badges per year at no cost. This makes digital credentialing accessible even for smaller programs.
The real cost savings come from efficiency. According to VerifyEd, University of Toronto's School of Continuing Studies saved 170 workdays and $170,000 in overhead costs after implementing digital credentials. These savings often offset platform fees.
Why Digital Diplomas Matter for Your Applications
When you apply to graduate school or a job, speed matters. Digital diplomas let you share verified credentials instantly.
You can add your credential to LinkedIn, email it directly to an admissions office, or include a verification link in your application materials. According to Temple University, digital diplomas can be shared on professional sites such as LinkedIn or emailed to employers.
Graduate programs often have tight deadlines. According to UC San Diego, priority posting is available for students who need their degrees posted to their academic records sooner due to graduate school admission, employment, military service, or participation in a specialized program. A digital diploma can help you meet these deadlines because it's available faster than a mailed paper copy.
Employers increasingly value instant verification. According to the National Student Clearinghouse, 64% of people said they had lied about skills, experience, or references at least once. Digital diplomas help employers confirm your credentials quickly and confidently.
What You Should Do
If you're currently enrolled or recently graduated:
Check with your registrar. Ask if your institution offers digital diplomas and how to obtain yours.
Verify your institution's accreditation. Use the U.S. Department of Education database to confirm your school is accredited by a recognized agency.
Download and store your credential. Once you receive your digital diploma, save it in multiple locations.
Learn the verification process. Know how to share your credential and explain the verification process to employers or graduate programs.
Keep your paper diploma too. Some situations may still require a physical document. Having both gives you flexibility.
If you're choosing a school:
Prioritize accreditation over format. A regionally accredited online program is better than an unaccredited in-person one.
Ask about digital credentials. Schools that offer digital diplomas are often more technologically current overall.
Research verification methods. Blockchain-secured credentials offer stronger protection than simple PDF files.
The Bottom Line
Digital diplomas are legitimate, widely accepted, and increasingly standard at U.S. universities. They offer real advantages: instant verification, permanent accessibility, and protection against loss or damage.
What matters is not whether your diploma is digital or paper. What matters is whether your degree comes from an accredited institution. Focus on accreditation first. The format of your credential is secondary.
As verification technology advances, digital diplomas will likely become the default. Understanding how they work now puts you ahead of applicants who don't.




 How to Pay for College in 2026: Costs, Aid, and Smart Planning
How to Pay for College in 2026: Costs, Aid, and Smart Planning
 The Role of Robotics in Developing Future-Ready College Students
The Role of Robotics in Developing Future-Ready College Students
 Undergraduate Research: How Students Join Labs Across Campus
Undergraduate Research: How Students Join Labs Across Campus
 Using AI to Succeed in College Science Courses
Using AI to Succeed in College Science Courses
 What Steps Should You Take to Become a University Tutor?
What Steps Should You Take to Become a University Tutor?